为什么使用React还需要使用别的框架来搭配?
React的核心是使用组件定义界面的表现,是一个View层的前端库,那么在使用React的时候我们通常还需要一套机制去管理组件与组件之间,组件与数据模型之间的通信。
为什么使用Redux?
Facebook官方提出了FLUX思想管理数据流,同时也给出了自己的实现来管理React应用。可是当我打开FLUX的文档时候,繁琐的实现,又臭又长的文档,实在难以让我有使用它的欲望。幸好,社区中和我有类似想法的不在少数,github上也涌现了一批关于实现FLUX的框架,比较出名的有Redux,Reflux,Flummox。
其中Redux的简单和有趣的编程体验是最吸引我的地方。
简单。和其它的FLUX实现不一样,Redux只有唯一的state树,不管项目变的有多复杂,我也仅仅只需要管理一个State树。可能你会有疑问,一个state树就够用了?这个state树该有多大?别着急,Redux中的Reducer机制可以解决这个问题。
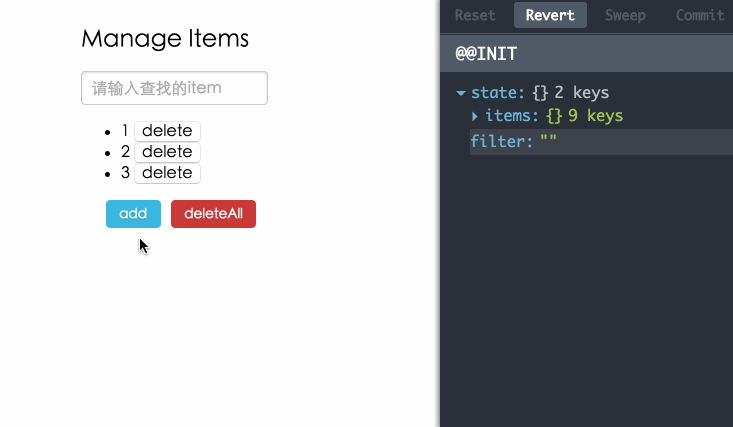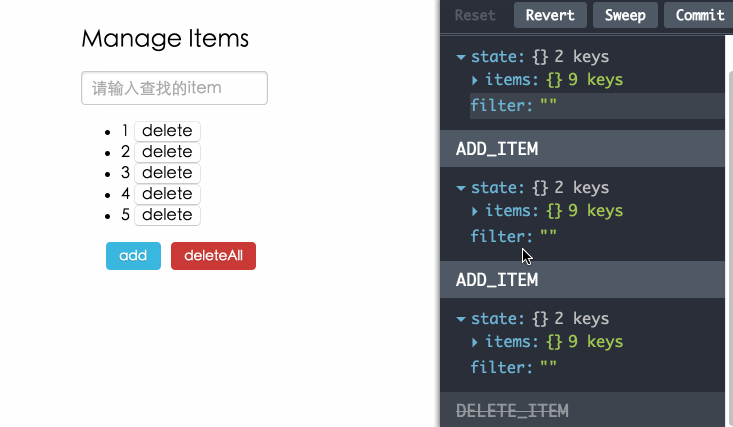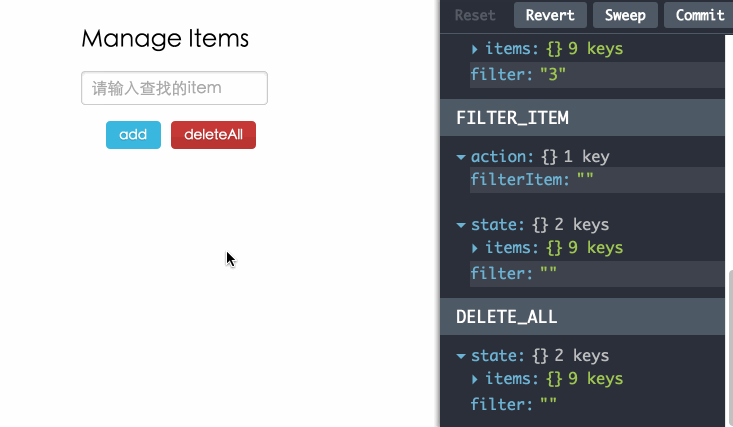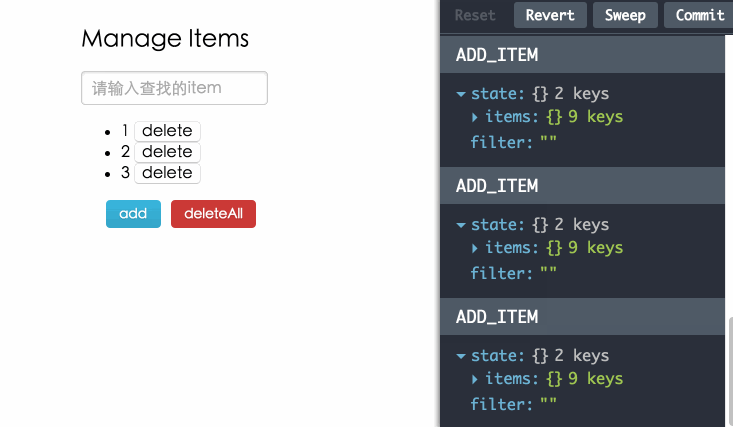
有趣。忙于迭代项目的你,体会编程带来的趣味是有多久没有体会到了?瞧下面这张图,右边那个调试工具是啥?整个应用的action和state都这么被轻松的管理了?行为还能被保存,删除,回滚,重置?修改了代码,页面不刷新也能产生变化?别开玩笑了,不行,世界那么大,让我去试试!
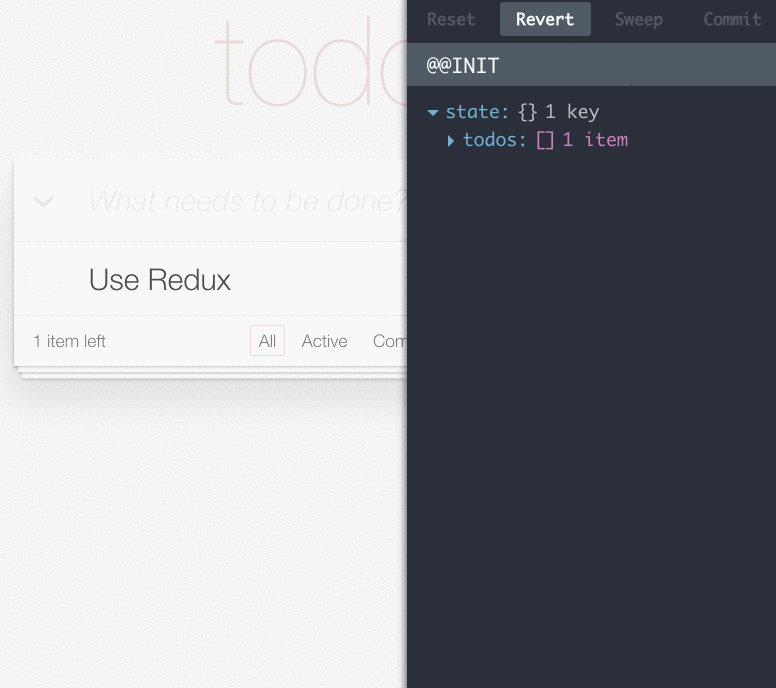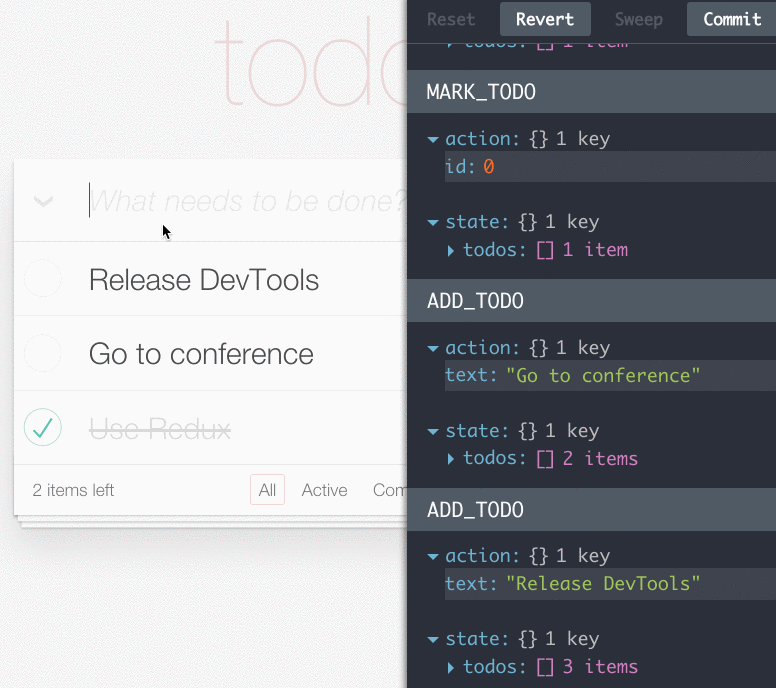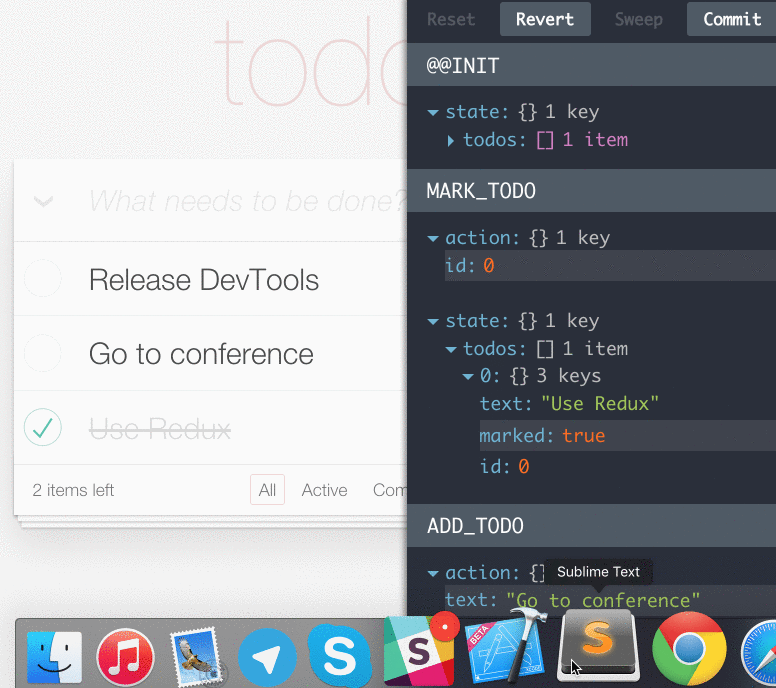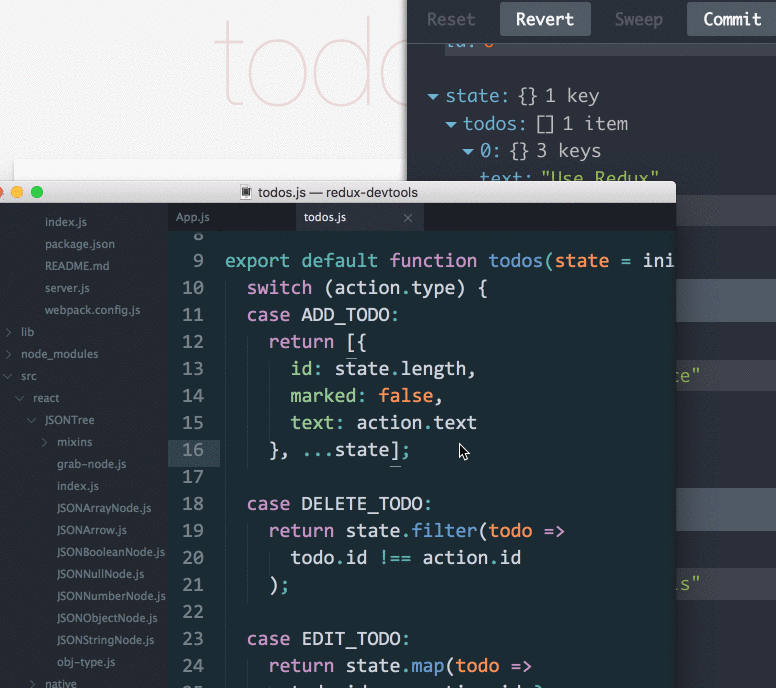
注:Redux开发调试工具:redux-devtools
React应用无刷新保存工具:hot-loader
不明真相的群众,可能这里需要我来安利一下Flux数据流的思想,看图:
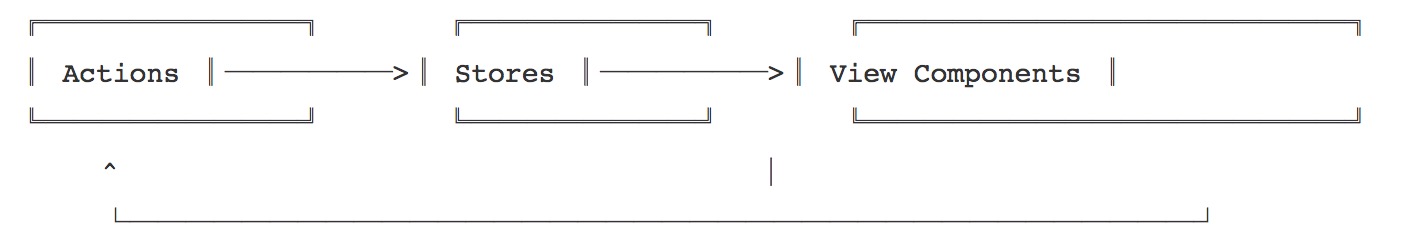
注意:图片仅仅是FLUX思想,而不是Facebook的实现。
大致的过程是这样的,View层不能直接对state进行操作,而需要依赖Actions派发指令来告知Store修改状态,Store接收Actions指令后发生相应的改变,View层同时跟着Store的变化而变化。
举个例子:A组件要使B组件发生变化。首先,A组件需要执行一个Action,告知绑定B组件的Store发生变化,Store接收到派发的指令后改变,那相应的B组件的视图也就发生了改变。假如C,D,E,F组件绑定了和B组件相同的Store,那么C,D,E,F也会跟着变化。
使用React和Redux开发一个小程序
为了更好的描述怎么样使用Redux管理React应用,我做了一个Manage Items的小例子。
目录结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| .
+-- app
| +-- actions
| +-- index.js
| +-- components
| +-- content.js
| +-- footer.js
| +-- searchBar.js
| +-- constants
| +-- ActionTypes.js
| +-- containers
| +-- App.js
| +-- reducers
| +-- index.js
| +-- items.js
| +-- filter.js
| +-- utils
| +-- configureStore.js
| +-- index.js
+-- css
| +-- pure.min.css
+-- index.html
|
Index.js
在入口文件中,我们需要把App和redux建立起联系。Provider是react-redux提供的组件,它的作用是把store和视图绑定在了一起,这里的Store就是那个唯一的State树。当Store发生改变的时候,整个App就可以作出对应的变化。{() => }是声明了一个返回的函数传进Provider的props.children里,这个方法将会在React的 0.14版本得到简化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import React from 'react';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import App from './containers/App';
import configureStore from './configureStore';
const store = configureStore();
React.render(
<div>
<Provider store={store}>
{() => <App /> }
</Provider>
</div>,
document.getElementById('app'));
|
Constants
keyMirror这个方法非常的有用,它可以帮助我们轻松创建与键值key相等的常量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import keyMirror from 'react/lib/keyMirror';
export default keyMirror({
ADD_ITEM: null,
DELETE_ITEM: null,
DELETE_ALL: null,
FILTER_ITEM: null
});
|
Actions
Action向store派发指令,action 函数会返回一个带有 type 属性的 Javascript Plain Object,store将会根据不同的action.type来执行相应的方法。addItem函数的异步操作我使用了一点小技巧,使用redux-thunk中间件去改变dispatch,dispatch是在View层中用bindActionCreators绑定的。使用这个改变的dispatch我们可以向store发送异步的指令。比如说,可以在action中放入向服务端的请求(ajax),也强烈推荐这样去做。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
import { ADD_ITEM, DELETE_ITEM, DELETE_ALL, FILTER_ITEM } from '../constants/actionTypes';
export function addItem(item) {
return dispatch => {
setTimeout(() => dispatch({type: ADD_ITEM}), 1000)
}
}
export function deleteItem(item, e) {
return {
type: DELETE_ITEM,
item
}
}
export function deleteAll() {
return {
type: DELETE_ALL
}
}
export function filterItem(e) {
let filterItem = e.target.value;
return {
type: FILTER_ITEM,
filterItem
}
}
|
Reducers
Redux有且只有一个State状态树,为了避免这个状态树变得越来越复杂,Redux通过 Reducers来负责管理整个应用的State树,而Reducers可以被分成一个个Reducer。
Reduce在javascript Array的方法中出现过,只是不太常用。简单快速的用代码样例来回顾一下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
var arr = [1,2,3,4];
var initialValue = 5;
var result = arr.reduce(function(previousValue, currentValue) {
return previousValue + currentValue
}, initialValue)
console.log(result)
|
回到Redux中来看,整个的状态就相当于从[初始状态]merge一个[action.state]从而得到一个新的状态,随着action的不断传入,不断的得到新的状态的过程。(previousState, action) => newState,注意:任何情况下都不要改变previousState,因为这样View层在比较State的改变时只需要简单比较即可,而避免了深度循环比较。Reducer的数据结构我们可以用immutable-js,这样我们在View层只需要react-immutable-render-mixin插件就可以轻松的跳过更新那些state没有发生改变的组件子树。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import Immutable from 'immutable';
import { ADD_ITEM, DELETE_ITEM, DELETE_ALL } from '../constants/actionTypes';
const initialItems = Immutable.List([1,2,3]);
export default function items(state = initialItems, action) {
switch(action.type) {
case ADD_ITEM:
return state.push( state.size !=0 ? state.get(-1)+1 : 1 );
case DELETE_ITEM:
return state.delete( state.indexOf(action.item) );
case DELETE_ALL:
return state.clear();
default:
return state;
}
}
|
连接reducers
Redux提供的combineReducers函数可以帮助我们把reducer组合在一起,这样我们就可以把Reducers拆分成一个个小的Reducer来管理Store了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import { combineReducers } from 'redux';
import items from './items';
import filter from './filter';
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
items,
filter
});
export default rootReducer;
|
Middleware
在Redux中,Middleware 主要是负责改变Store中的dispatch方法,从而能处理不同类型的 action 输入,得到最终的 Javascript Plain Object 形式的 action 对象。
以redux-thunk为例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
export default function thunkMiddleware({ dispatch, getState }) {
return next =>
action =>
typeof action === ‘function’ ?
action(dispatch, getState) :
next(action);
}
|
当ThunkMiddleware 判断action传入的是一个函数,就会为该thunk函数补齐dispatch和getState参数,否则,就调用next(action),给后续的Middleware(Middleware 插件可以被绑定多个)得到使用dispatch的机会。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import { compose, createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import rootReducer from './reducers';
var buildStore = compose(applyMiddleware(thunk), createStore)
export default function configureStore(initialState) {
return buildStore(rootReducer, initialState);
}
|
UI
智能组件和木偶组件,因为本文主要是介绍Redux。本项目中在结构上会把智能组件放在containers中,木偶组件放于components中。
containers
智能组件,会通过react-redux函数提供的connect函数把state和actions转换为旗下木偶组件所需要的props。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
import React from 'react';
import SearchBar from '../components/searchBar';
import Content from '../components/content';
import Footer from '../components/footer';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import ImmutableRenderMixin from 'react-immutable-render-mixin';
import * as ItemsActions from '../actions';
import { bindActionCreators } from 'redux';
let App = React.createClass({
mixins: [ImmutableRenderMixin],
propTypes: {
items: React.PropTypes.object,
filter: React.PropTypes.string
},
render() {
let styles = {
width: '200px',
margin: '30px auto 0'
}
const actions = this.props.actions;
return (
<div style={styles}>
<h2>Manage Items</h2>
<SearchBar filterItem={actions.filterItem}/>
<Content items={this.props.items} filter={this.props.filter} deleteItem={actions.deleteItem}/>
<Footer addItem={actions.addItem} deleteAll={actions.deleteAll}/>
</div>
)
}
})
export default connect(state => ({
items: state.items,
filter: state.filter
}), dispatch => ({
actions: bindActionCreators(ItemsActions, dispatch)
}))(App);
|
components
木偶组件,各司其职,没有什么关于actions和stores的依赖,拿出项目中也可独立使用,甚至可以和别的actions,stores进行绑定。
- SearchBar:查找Item。
- Content:控制Items的显示,删除一个Item。
- Footer:新增Item,删除全部Item。
调试工具
使用redux-devtools调试,为你在开发过程中带来乐趣。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
function renderDevTools(store) {
if (__DEBUG__) {
let {DevTools, DebugPanel, LogMonitor} = require('redux-devtools/lib/react');
return (
<DebugPanel top right bottom>
<DevTools store={store} monitor={LogMonitor} />
</DebugPanel>
);
}else {
return null;
}
}
React.render(
<div>
<Provider store={store}>
{() => <App /> }
</Provider>
{renderDevTools(store)}
</div>,
document.getElementById('app'));
var buildStore;
if(__DEBUG__) {
buildStore = compose(
applyMiddleware(thunk),
require('redux-devtools').devTools(),
require('redux-devtools').persistState(window.location.href.match(/[?&]debug_session=([^&]+)\b/)),
createStore
)
}else {
buildStore = compose(applyMiddleware(thunk), createStore)
}
export default function configureStore(initialState) {
return buildStore(rootReducer, initialState);
}
|
在你的代码中加上上面的两段代码,运行npm run debug命令,就可以用调试工具来管理你的项目了。


